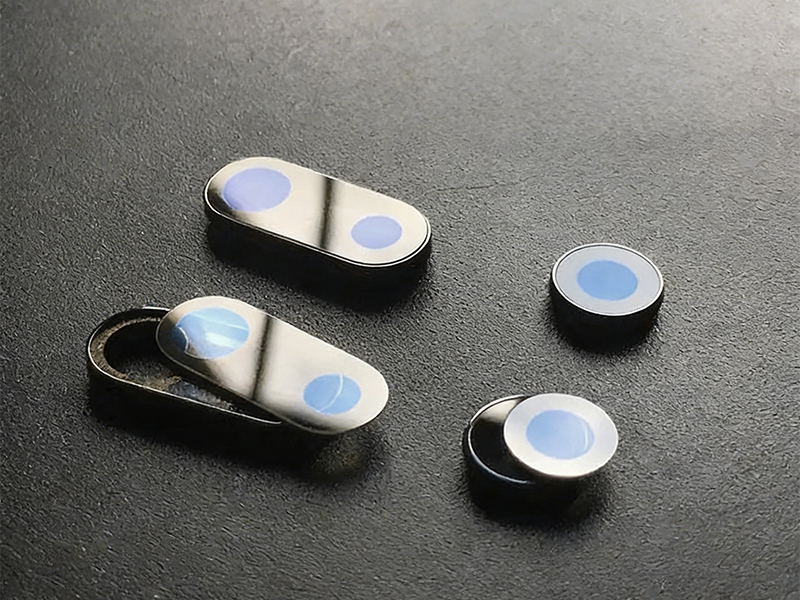
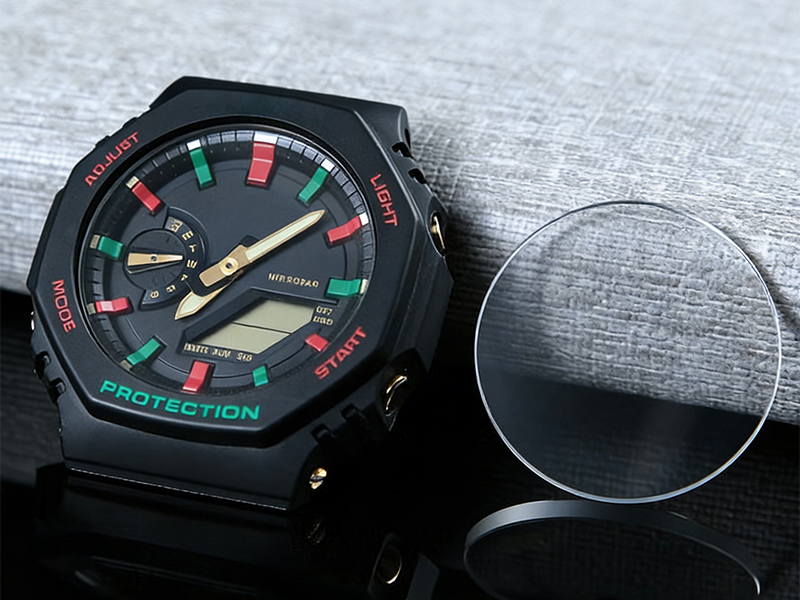
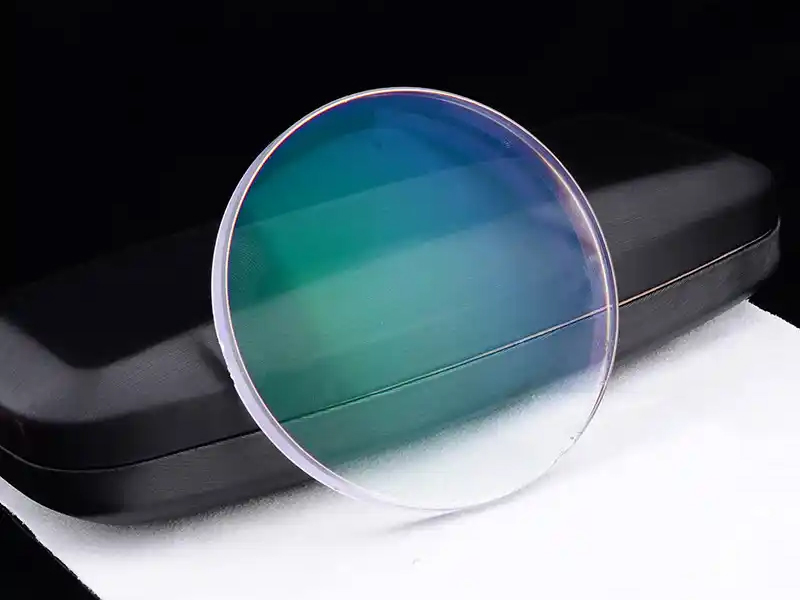
Sapphire (single-crystal Al?O?) and silicon carbide (SiC) are key substrates for high-performance electronic, optoelectronic, and precision optical devices due to their high hardness, thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and optical transparency. However, traditional processing methods often lead to chipping, microcracks, and tool wear, affecting yield and iteration speed. Therefore, laser processing, with its non-contact and high-precision advantages, has become a core solution, enabling processes such as cutting, dicing, and drilling, transforming these difficult-to-process materials into high-value components.
 Mr. cqchuke
Mr. cqchuke